Publication date: 24/11/14
ThemesNews
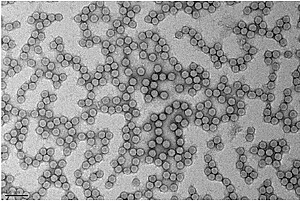
To infect a host cell and multiply, some viruses (such as hepatitis C) infiltrate ribosomes, large molecular machines found within every cell and linking proteins together. Through the process, cellular proteins are replaced by viral proteins. Strasbourg scientists have demonstrated that the essential component for certain viral infections - among the ribosome’s 80 components - is actually not necessary to normal cell function. This finding could lead to the development of new therapeutic strategies.